衛星大地測量作業四
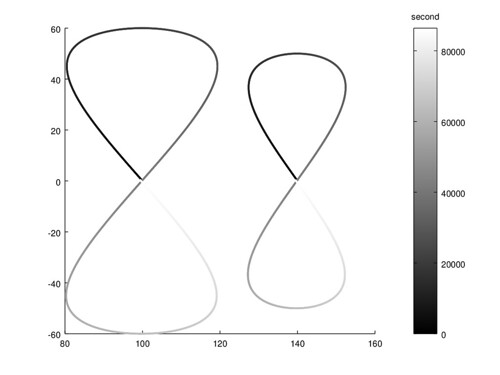
用線性化的公式假設軌道為圓計算衛星軌道投影在地面的軌跡。
根據黃金維老師講義中單元二附錄 C 的計算流程:
C20 = 108263E-8;
GM = 397778481800000;
earth_rotation_speed = 7.292115147*10^-5;
if (!exist('a'))
a = input('major-axis of satellite orbit (m): ');
end
if (!exist('i') || iscomplex(i))
i = input('inclination angle of satellite orbit (rad): ');
end
if (!exist('lon0'))
lon0 = input('longitude when satellite cross equator (rad): ');
end
mean_earth_radius = 6371000;
ae = mean_earth_radius;
we = earth_rotation_speed;
n = @(a) GM^0.5/a^1.5;
perigee_argument_speed = @(e, a, i) (
3*n(a)*C20*ae^2 /
(4*(1-e^2)^2*a^2) *
(1 - 5*cos(i)^2)
);
ascending_node_speed = @(e, a, i) (
3*n(a)*C20*ae^2 /
(2*(1-e^2)^2*a^2) *
cos(i)
);
mean_anomaly_speed = @(e, a, i) (
n(a) - 3*n(a)*C20*ae^2 /
(4*(1-e^2)^1.5*a^2) *
(3*cos(i)^2-1)
);
function plot_xy_gradiant_color(x, y, color)
surface([x' x'], [y' y'], [color' color'],
'LineWidth', 2,
'EdgeColor', 'flat');
end
function plot_xy_time(x, y, time)
plot_xy_gradiant_color(x, y, time);
hx = colorbar();
title(hx, 'second');
end
u_dot = perigee_argument_speed(0, a, i) + mean_anomaly_speed(0, a, i);
ome_dot = ascending_node_speed(0, a, i);
sample_count = 360;
time_tic = longitude = latitude = zeros(1, sample_count);
count = 1;
lt = longitude;
wt = longitude;
for t = 0:60:86400
u = mod(t*u_dot, pi*2);
time_tic(count) = t;
lat = asin(sin(i)*sin(u));
if (i<=pi/2)
latitude(count) = lat;
else
latitude(count) = -lat;
end
if (i<pi/2)
sign = 1;
else
sign = -1;
end
lambda_t = sign*atan(abs(cos(i)) * tan(u));
lt(count) = lambda_t;
wt(count) = t*(we-ome_dot);
if (u > pi/2 && u < pi/2*3)
lambda_t += pi;
end
lon = lon0 + lambda_t - t*(we-ome_dot);
if (lon > pi*2 || lon < 0)
lon = mod(lon, pi*2);
end
longitude(count) = lon;
count+=1;
end
plot_xy_time(longitude*180/pi, latitude*180/pi, time_tic);
if (exist('output_image'))
print('-dpng', output_image);
end
其中單位是用公尺、公斤、弧度, 做圖時再轉換回角度。