平差作業九
平差 GNSS 基線後的誤差橢圓計算。
變方協變方矩陣
平差過程與第八次作業大致相同,就不再列式, 直接進入間接觀測平差後,可以計算得所有未知數的變方協變方矩陣。
\hat \Sigma _ {\hat x} = \hat {\sigma_0} N^{-1} = \
\begin{bmatrix}
\sigma_{X_A} ^2 & \sigma_{X_A Y_A} & \dots \\
\sigma_{X_A Y_A} & \sigma_{Y_A} ^2 & \dots \\
\vdots
\end{bmatrix}
協變方矩陣中,各元素是變方或二未知數的協變方。 單一點上的 x y 座標的變方協變方矩陣, 就是其中的一小區塊。
%% xy_matrix(3) 就是取出第三點的 X Y 相關矩陣
xy_matrix = @(i) point_covariance_matrix(i*3-2:i*3-1, i*3-2:i*3-1);
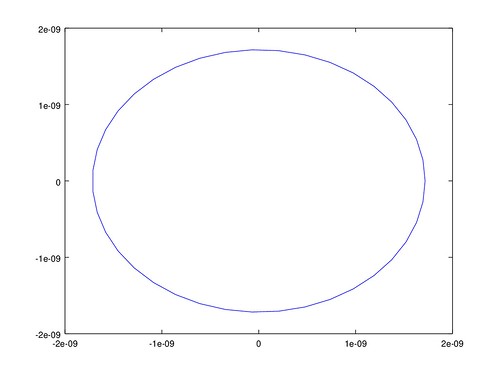
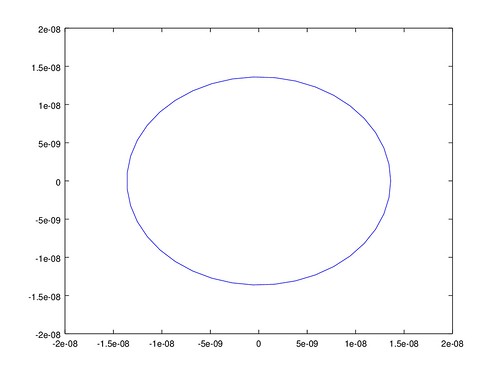
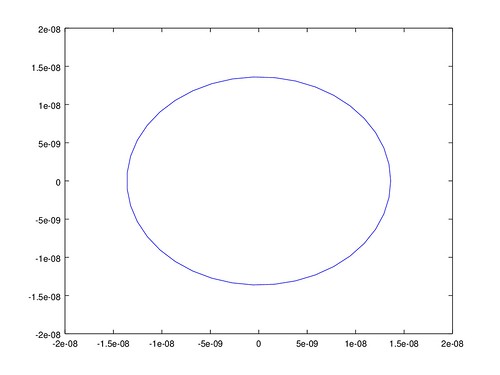
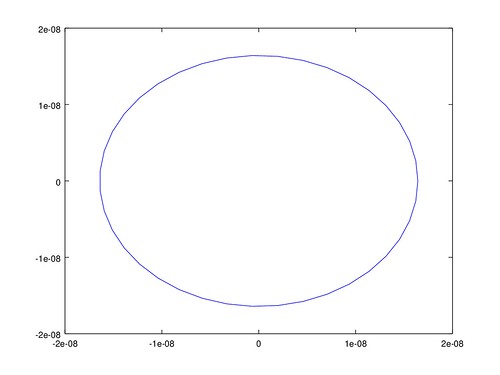
誤差橢圓
有了 x y 的協變方矩陣,就能計算平面上的誤差橢圓。 誤差橢圓可以用三個參數表示, 分別是橢圓的長軸長、短軸長、長軸角度。
C_1 = \hat {\sigma_0} \sqrt \lambda_1 \\
C_2 = \hat {\sigma_0} \sqrt \lambda_2 \\
\theta = \frac{1}{2} arctan (
\frac { 2 \sigma_{x y} } {\sigma_x^2 - \sigma_y^2} )
function elips_parameter = compute_error_elips(xy_covariance, sigma0)
eigenvalue = eig(xy_covariance);
elips_parameter = zeros(1, 3);
elips_parameter(1:2) = sqrt(eigenvalue(1:2)) * sigma0;
orintation2 = atan2(
2*xy_covariance(1,2),
(xy_covariance(1,1) - xy_covariance(2,2))
);
elips_parameter(3) = orintation2 / 2;
end
繪圖
要從橢圓參數畫出誤差橢圓,我是用參數式與 sin cos 計算。
function xy = compute_ellipse_xy(long, short, orientation)
m = 40;
x = zeros(m,1);
y = zeros(m,1);
theta = linspace(0,2*pi,m);
for k = 1:m
x(k) = long * cos(theta(k));
y(k) = short * sin(theta(k));
end
alpha = -orientation;
R = [cos(alpha) -sin(alpha)
sin(alpha) cos(alpha)];
rCoords = R*[x' ; y'];
xr = rCoords(1,:)';
yr = rCoords(2,:)';
xy = [xr'; yr'];
end
function plot_name(todo, file)
fig = figure('visible', 'off');
todo();
print('-dpng', file);
close(fig);
end
for i = 1:rows(point_vector)
elips_parameter = compute_error_elips(
xy_matrix(i), variance_post);
elips_xy = compute_ellipse_xy(
elips_parameter(1),
elips_parameter(2),
elips_parameter(3));
plot_name(@() plot(elips_xy(1,:), elips_xy(2,:)),
['ellipse-' num2str(i) '.png']);
end
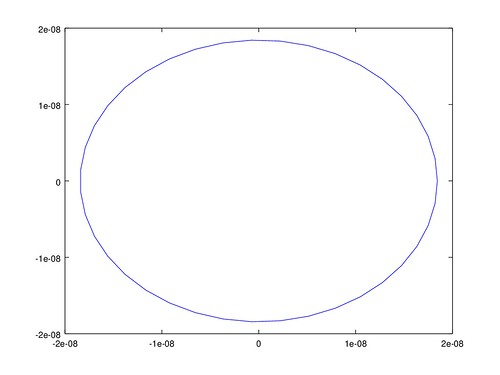
但繪圖結果中的 X Y 座標軸好像不一致, 所以看起來變成橢圓,其實都是正圓。 從協變方矩陣中各點的 $\sigma_{x y}$ 都為 0, 也就是各點的 x y 座標無相關, 誤差橢圓的長短軸等長,即為正圓。